Paraxcel¶
Quick Summary
Paraxcel A lightweight, local-first Python desktop application using Tkinter to convert Microsoft Word DOCX files containing multiple-choice questions into structured Excel spreadsheets.
- Context:
Python,Tkinter,Pandas,Pydantic,python-docx,Solo Project,Feb-Mar 2025 - Role: Sole developer responsible for design, implementation, testing, documentation, and packaging of the application.
- Impact: Created a tool that automates the extraction of questions and answers from DOCX files, reducing manual data entry time for educators and content creators, by implementing parsing logic with
python-docxand structuring output withpandas.
Overview¶
Paraxcel is a Python desktop application built with Tkinter that addresses the need for converting multiple-choice questions from DOCX files into an organized Excel format, it targets educators, content creators, and assessment professionals who need to manage question banks efficiently. The application provides a simple graphical user interface for file selection and conversion, running entirely locally.
Goals¶
The primary goals for the Paraxcel project were:
- To automate the tedious and time-consuming manual process of extracting multiple-choice questions and their corresponding answers from Microsoft Word documents.
- To structure the extracted data into a usable and organized Excel format.
- To create a simple, reliable, and accessible desktop tool for educators and content creators.
Responsibilities¶
- Designed the application architecture, including module separation (
docx_parser,excel_writer,model,para_utility,interface) for maintainability and scalability. - Implemented robust
DOCXparsing usingpython-docxto accurately extractquestions,answer options, and identify thecorrect answerbased on formatting (color/highlight). - Utilized pandas to structure extracted data into a standardized, clean format, enabling reliable export to
.xlsxfiles. - Built a user-friendly graphical interface with
Tkinter, enabling users to easily select input files/folders and initiate the conversion process. - Integrated Pydantic for rigorous data validation of extracted question data, ensuring data integrity before export.
- Created essential utility functions (
para_utility.py) for text cleaning, format handling, and precise answer detection. - Authored comprehensive technical (
doc.md) and user (README.md) documentation. - Packaged the application into a standalone executable using
PyInstallerfor straightforward distribution and use on Windows.
Technologies Used¶
- Languages: Python
- GUI: Tkinter (Standard Python library) - For building the desktop graphical interface.
- DOCX Parsing:
python-docx- For reading and analyzing.docxfile content. - Data Handling & Excel Export:
pandas- For structuring the extracted data and writing to.xlsxfiles. - Data Validation:
Pydantic- For validating the structure and types of extracted question data. - Documentation:
Markdown- ForREADME.mdanddoc.md.
Tools
- Version Control: Git
- Packaging: PyInstaller - For creating the standalone executable.
- Development Environment: VS Code
Process¶
The development process involved identifying the need for a simple DOCX-to-Excel conversion tool for MCQs and followed a structured approach focused on modularity and ease of use.
- Requirement Gathering: Defined the core functionality: parse DOCX files containing questions followed by four options and export them to Excel, including support for detecting marked answers.
- Technology Stack Selection: Chose libraries (
python-docx,pandas,Tkinter,Pydantic) best suited for the task, balancing functionality with ease of deployment (local-first, standard libraries). - Modular Implementation: Developed each component (
parsing,writing,GUI,validation) as a distinct module. - Testing & Refinement: Used sample files to rigorously test parsing accuracy and output format.
- Documentation: Created user and technical guides to support adoption and understanding.
- Packaging: Prepared the application for distribution as a single executable.
Recognition¶
I am proud to share that I have successfully completed the CS50x - Introduction to Computer Science course.
Certificate¶
 Challenges &
Challenges &  Solutions¶
Solutions¶
-
Handling Varied DOCX Formatting
Parsing semi-structured DOCX files presented challenges due to inconsistencies in formatting, numbering, and spacing. Reliably detecting the correct answer based on subtle formatting like font color or highlighting was a key challenge.
Developed flexible parsing logic (
parse_para) designed to accommodate common variations. Implemented specialized utility functions (remove_prefix,find_marked_answer) that leverage python-docx's capabilities to accurately identify marked answers by inspecting run-level formatting properties. Documented input format expectations clearly to guide users.
-
Ensuring Data Quality and Consistency
Extracting data from a semi-structured format like DOCX risked incomplete or malformed records before export.
Integrated Pydantic models (
Question) to enforce a strict schema for extracted data. This validation step acts as a safeguard, ensuring that only correctly structured and typed data proceeds to theExcelexport, preventing errors and ensuring reliable output.
-
Creating an Accessible Tool for Non-Technical Users
The goal was a tool usable by educators without programming knowledge, requiring a simple interface and easy installation.
Built a straightforward and intuitive GUI using Tkinter, Python's standard library, minimizing external dependencies. Used
PyInstallerto bundle the application and all its dependencies into a single, easy-to-distribute executable (paraxcel.exe), significantly lowering the barrier to entry for end-users.
Achievements¶
- Developed and launched Paraxcel, a functional desktop application, automating the conversion of MCQs from DOCX to a structured Excel format.
- Implemented advanced parsing features, including the ability to detect correct answers based on font color or highlighting within the DOCX file.
- Incorporated basic text formatting handling (superscript/subscript) during extraction for improved data fidelity.
- Provided clear, user-focused documentation (
README.md) and technical insights (doc.md). - Packaged the application into a convenient standalone executable using PyInstaller, simplifying deployment and usage.
Impact: Enabled educators and content creators to save significant time and effort (quantified by reduced manual data entry hours) previously spent on manual data entry.
Key Learnings¶
- Gained practical experience using the
python-docxlibrary to parse the structure and formatting of Word documents programmatically. - Developed skills in building simple desktop GUIs with Python's built-in
Tkinterlibrary. - Applied
Pydanticfor robust data validation in a data processing pipeline. - Utilized
pandasfor efficient data structuring and exporting to Excel formats. - Learned the process of packaging Python applications into standalone executables using
PyInstaller, including handling dependencies and data files. - Understood the challenges and importance of defining clear input format expectations when parsing semi-structured documents like DOCX.
Outcomes¶
- A working, local-first desktop application (
paraxcel.exe) capable of converting DOCX files (containing questions and 4 options) into structured Excel (.xlsx) files. - Source code is available on GitHub, along with documentation and sample files.
- A video demonstration showcasing the application's functionality.
Visuals¶
Docx Input
Q1. What is the capital of France?
A. Berlin
B. Madrid
C. Paris (Highlighted as correct)
D. Rome
✅ Excel Output
| Question | Option 1 | Option 2 | Option 3 | Option 4 | Answer Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| What is the capital of France? | Berlin | Madrid | Paris | Rome | 3 |
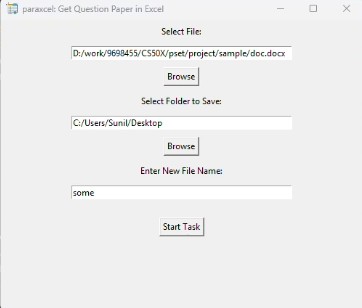
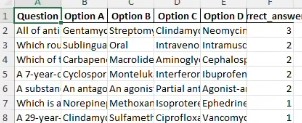
🖼️ Screenshots¶
Paraxcel Tkinter GUI showing file/folder selection fields and buttons.
Sample input DOCX file snippet showing question/option format.
Resulting Excel file snippet showing structured data.
🔗 Video Demo¶
Links¶
Conclusion¶
Paraxcel successfully provides a targeted solution for automating the often tedious task of extracting multiple-choice questions from DOCX files into a more usable Excel format. By leveraging libraries like python-docx, pandas, Pydantic, and Tkinter, the project delivers a functional, easy-to-use desktop tool for educators and content creators. Key takeaways include the practical application of these libraries for document parsing, data handling, validation, GUI development, and application packaging, resulting in a useful utility that addresses a specific workflow challenge.
AI Skill Assessment
Prompt1 Source
Strengths¶
- Python Application Development: Proven ability to design, develop, and package a complete, modular desktop application.
- GUI Development (Tkinter): Experience building functional graphical interfaces for user interaction.
- Document Parsing & Data Processing: Skilled in extracting structured data from complex document formats (
.docx) and processing it usingpandas. - Data Validation: Practical application of
Pydanticfor ensuring data integrity and correctness. - Comprehensive Documentation: Ability to create clear technical and user-focused documentation.
- Application Packaging & Distribution: Experience using
PyInstallerfor creating standalone executables and managing dependencies. - CI/CD Implementation: Basic experience setting up automated workflows for testing, security checks, and builds using GitHub Actions.
- Software Reliability Basics: Inclusion of testing tools and security scanning indicates an understanding of foundational quality practices.
Areas for Improvement¶
- Testing Depth: Expanding test coverage and visibility would further strengthen quality assurance processes.
- Advanced Error Handling: Implementing more granular logging and exception handling could enhance application robustness.
- Performance Optimization: Exploring techniques for handling very large files more efficiently could improve scalability.
- UI/UX: For projects requiring more complex interfaces, exploring modern GUI frameworks might be beneficial.
- Cross-Platform Deployment: Expanding build support beyond Windows would increase application accessibility.
Relevant Roles¶
Strong Fit¶
- Python Application Developer: Directly aligns with the project's nature.
- Automation Engineer: Demonstrates strong skills in automating data extraction and processing workflows.
Good Fit¶
- Backend Developer (Data Focus): Relevant experience in data parsing, validation, and structuring.
- Junior DevOps/Build Engineer: Basic experience with CI/CD automation and application packaging.
Less Direct Fit¶
- Frontend Web Developer: No web technology experience shown.
- Data Scientist/ML Engineer: Project focuses on extraction, not analysis or modeling.
- Senior DevOps/SRE: Lacks infrastructure, monitoring, or cloud services.
- Mobile Developer: No mobile development experience shown.
Conclusion¶
This project effectively showcases capabilities in end-to-end Python application development, particularly in document processing, data handling, and automation. The inclusion of data validation, packaging, and basic CI/CD demonstrates a well-rounded approach to software development. This experience is highly relevant for roles focused on Python application development, automation, and data processing pipelines.
-
This AI skill assessment was generated based on the skill-assessment-prompt.md and the provided project documentation. It is intended as an illustrative summary and should be interpreted in the context of the available code and documentation in codebase. ↩