GSTN Hackathon: Predictive Binary Classification Project¶
Quick Summary
GSTN Hackathon: Predictive Binary Classification Developed a robust, interpretable machine learning pipeline for binary classification on anonymized GSTN data, focusing on model performance, compliance, and reproducibility.
- Context:
Sep 2024,Python,scikit-learn,XGBoost/LightGBM,pandas,matplotlib,Jupyter, solo project for GSTN Hackathon. - Role: Sole developer—handled all phases: EDA, feature engineering, model selection, hyperparameter tuning, evaluation, and documentation.
- Impact: Achieved >97% accuracy and strong F1/MCC on imbalanced GSTN data by designing a reproducible, competition-compliant pipeline with anonymized model/code and no data leakage.
Overview¶
This project was developed for the GSTN Hackathon, aiming to build a high-performance, interpretable binary classification model on a large, anonymized GSTN dataset. The solution strictly adheres to competition rules: all model names and parameters are anonymized/randomized, and no original or derivative datasets are included in the repository.
The workflow covers the full ML lifecycle: data integrity checks, EDA, preprocessing, feature engineering, model selection (tree-based models), hyperparameter tuning (GridSearchCV, Bayesian Optimization), cross-validation, threshold optimization, and comprehensive evaluation/reporting.
Recent updates:
- Final model and code anonymized for submission.
- All data files excluded for compliance.
- Extensive documentation and reproducibility scripts added.
About the GSTN Hackathon
The Government of India hosted an AI/ML-based Hackathon to develop predictive models for GST analytics. This initiative was designed to engage students, researchers, and professionals in designing innovative AI/ML solutions using a large, anonymized dataset of approximately 900,000 records with 21 attributes.
Key Details¶
- Participation: Open to Indian students, researchers, and professionals from academia, startups, or companies.
- Registration: Required sign-up via Janparichay and submission of participant details.
- Teams: Up to five members per team, with one team lead required. Solo participation was allowed.
Hackathon Structure¶
Online Phase¶
- Dataset Access: Participants received anonymized, labeled datasets for training and testing.
- Problem Statement:
Given: Dtrain: Training data matrix (m × n)Dtest: Test data matrix (m₁ × n)Ytrain: Target variable for training (m × 1)Ytest: Target variable for testing (m₁ × 1)- Objective:
Construct a predictive model Fθ(X) → Ypred that accurately estimates the target variable Y for new, unseen inputs X.
Workflow Steps¶
- Model Construction:
Define a predictive function Fθ(X) parameterized by θ to map input features X to predicted outputs Ypred, capturing the relationship between features and target variable. - Training:
Optimize model parameters θ by minimizing a loss function L(Y, Fθ(X)) using Dtrain. Feature engineering and selection were encouraged to enhance performance. - Testing:
Apply the optimized model Fθ*(X) to Dtest to generate predictions Ypred for each input Xj. - Performance Optimization:
Evaluate model performance using metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and AUC-ROC. Refine the model iteratively to improve these metrics. - Submission:
Submit predicted outputs Ypred_test along with: - Source code (preferably on GitHub)
- A detailed report (modeling approach, code comments, citations, evaluation metrics, and key performance indicators)
Offline Phase¶
- Shortlisting:
Top 9–15 teams were shortlisted based on initial evaluation. - Final Round:
Shortlisted teams refined their models using additional data and SME feedback, then presented their solutions and participated in interviews with the jury in Delhi.
Evaluation & Jury¶
- Jury Composition:
Senior data scientists, tax administration experts, academic professionals, and representatives from GSTN and NIC. - Evaluation Process:
- Initial Screening: Compliance and basic functionality check.
- Technical Evaluation: Assessment of model performance, innovation, and robustness.
- Practical Usability: Evaluation of real-world applicability.
- Decision Making:
Prizes awarded to top three teams; special prize for all-women teams. Consolation prizes at jury’s discretion. The jury’s decision was final.
Timeline¶
- Submission Period: August 12, 2024 – October 12, 2024
- Hackathon Duration: 45 days (from registration to final submission)
Goals¶
- Build a robust, interpretable binary classifier for GSTN data.
- Address severe class imbalance and missing values.
- Ensure reproducibility and compliance with competition/legal requirements.
- Provide clear documentation and visualizations for model transparency.
Responsibilities¶
- Led all stages: EDA, feature engineering, model selection, tuning, evaluation, and reporting.
- Designed and implemented utility functions for cross-validation, threshold optimization, and evaluation.
- Automated model training, saving, and reproducibility via scripts and notebooks.
- Created all documentation, visualizations, and presentation materials.
- Ensured strict compliance with anonymization and data handling rules.
Technologies Used¶
- Languages: Python
- Libraries/Frameworks:
- pandas, numpy (data manipulation)
- scikit-learn (modeling, metrics, pipelines)
- XGBoost, LightGBM (tree-based models)
- imbalanced-learn (SMOTE, RUS)
- matplotlib, seaborn (visualization)
- joblib (model persistence)
- SHAP (model explainability)
- Tools:
- Jupyter Notebook (EDA, prototyping)
- Markdown (documentation)
- Git (version control)
Tools
- dask (optional, for large data)
- scikit-optimize (Bayesian optimization)
- Google Colab (cloud prototyping)
Process¶
- Data Integrity: Verified dataset integrity using SHA256 checksums.
- EDA: Explored distributions, missing values, outliers, and feature correlations.
- Preprocessing: Median imputation for missing values, outlier handling (Winsorization), feature selection via correlation and statistical tests.
- Modeling: Compared Logistic Regression, Random Forest, XGBoost, LightGBM; focused on tree-based models for best performance.
- Imbalance Handling: Used Random Under Sampling (RUS) and SMOTE; tuned
scale_pos_weightfor tree models. - Hyperparameter Tuning: Employed GridSearchCV and Bayesian Optimization for optimal parameters.
- Evaluation: Used stratified k-fold cross-validation, optimized threshold for F1, and computed metrics (Accuracy, F1, MCC, ROC-AUC, etc.).
- Explainability: Analyzed feature importance and SHAP values.
- Reporting: Documented all steps, results, and compliance measures.
Selection & Recognition¶
- Selection: This project, developed as a single-member (solo) team, was selected for the interview and presentation round—ranking among the top 17 teams out of more than 200 participating teams (most of which were multi-member).
- Recognition: Received a certificate and prize for reaching the final round.
- Note: Unfortunately, the competition did not proceed beyond the interview/presentation stage due to unknown or unsatisfactory results for the GSTN Hackathon organizers.
Certificate¶
 Challenges &
Challenges &  Solutions¶
Solutions¶
-
Severe Class Imbalance
91%/9% class split risked model bias.
Used RUS, SMOTE, and tuned
scale_pos_weightto balance classes and maximize recall/F1.
-
Missing Values & Outliers
Columns with >50% missing; outliers in many features.
Dropped high-missing columns, used median imputation, and Winsorized outliers.
-
Data Leakage Risk
Potential for train-test contamination and target leakage.
Strict separation of train/test, careful pipeline design, and validation of all preprocessing steps.
-
Compliance & Anonymization
Competition required anonymized model names/params and no data sharing.
Before sharing code and documentation publicly, randomized/anonymized all model identifiers and parameters; excluded all data files.
Achievements¶
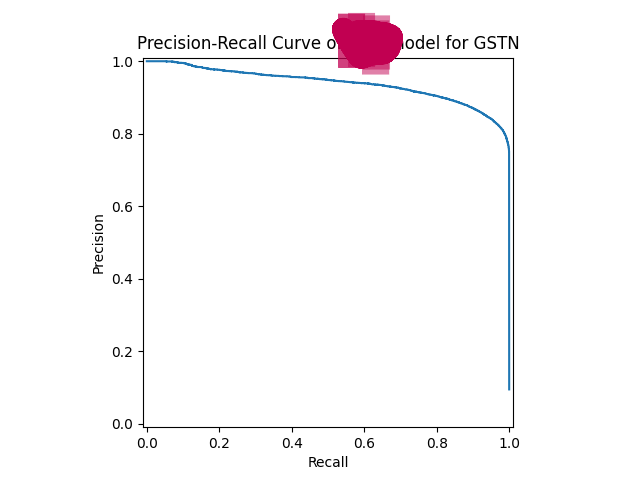
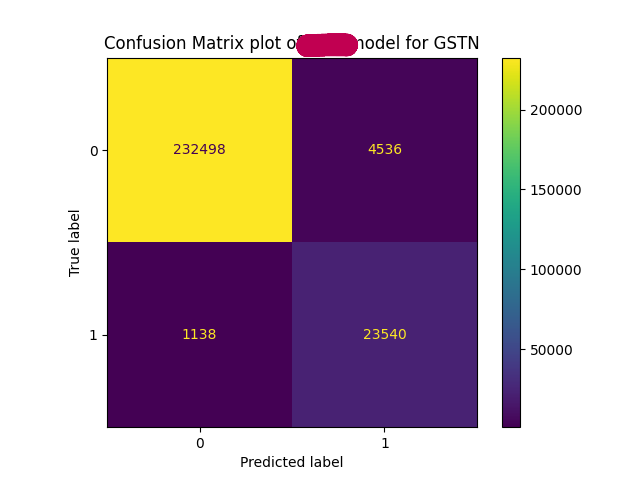
- Accomplished >97% accuracy and strong F1/MCC on imbalanced GSTN data, as measured by cross-validation and test set metrics, by designing a robust, reproducible ML pipeline.
- Delivered a fully anonymized, competition-compliant codebase with clear documentation and reproducibility scripts.
- Produced comprehensive visualizations and reports for model transparency.
Key Learnings¶
- Advanced techniques for handling class imbalance in real-world datasets.
- Importance of strict data handling to prevent leakage and ensure reproducibility.
- Practical experience with hyperparameter tuning (GridSearchCV, Bayesian Optimization) and model explainability (SHAP).
- Effective communication of technical results through documentation and presentations.
Outcomes¶
- Final model achieved:
- Accuracy: ~97.8%
- F1 Score: ~0.89
- MCC: ~0.88
- ROC-AUC: ~0.99
- All results reproducible via provided scripts (with user-supplied data).
- Project recognized for compliance and transparency in hackathon setting.
Visuals¶
Links¶
Conclusion¶
This project demonstrates a full-cycle, competition-compliant approach to binary classification on challenging, imbalanced, and anonymized data. Key outcomes include high model performance, robust handling of data issues, and strict adherence to legal/competition requirements. The experience reinforced best practices in reproducibility, compliance, and transparent ML development.
AI Skill Assessment
Prompt1 Source
Strengths¶
-
Comprehensive ML Workflow Implementation
- Demonstrates end-to-end machine learning pipeline: data integrity checks, EDA, preprocessing, feature engineering, model selection, hyperparameter tuning (GridSearchCV, Bayesian Optimization), cross-validation, threshold optimization, and evaluation.
- Uses advanced techniques for imbalanced data (SMOTE, RUS,
scale_pos_weight). - Implements robust evaluation with stratified k-fold cross-validation and threshold tuning for F1 optimization.
-
Reproducibility & Compliance
- All code and documentation are anonymized for competition compliance; no data files are included, and model identifiers are randomized.
- Clear instructions for reproducibility, including requirements files and explicit notes on data paths.
-
Documentation & Communication
- Extensive, well-structured documentation in Markdown: project overview, goals, process, challenges, achievements, and visuals.
- Visual aids (precision-recall curve, confusion matrix, feature importance) are generated and referenced.
- Presentation and storytelling materials are included, showing strong communication skills.
-
Automation & Utility Functions
- Modular utility functions for cross-validation, threshold finding, evaluation, and plotting.
- Scripts and notebooks automate model training, saving, and evaluation.
-
Model Explainability
- Uses SHAP for feature importance and model transparency.
- Reports and presentations highlight interpretability and explainability.
-
Attention to Data Integrity
- SHA256 checks for data integrity.
- Careful handling of missing values, outliers, and prevention of data leakage.
Areas for Growth¶
-
Testing & CI/CD
- No evidence of automated unit/integration tests or CI/CD pipelines (e.g., GitHub Actions, pytest).
- Adding tests for utility functions and model evaluation would improve robustness.
-
Security & Data Privacy
- While compliance is strong, there is no mention of secure handling of sensitive data or privacy-preserving ML techniques (beyond anonymization).
-
Scalability & Deployment
- No deployment scripts, Dockerfiles, or cloud deployment instructions.
- No evidence of API endpoints or serving models in production.
-
Software Engineering Practices
- No use of type hints, code linting, or static analysis tools.
- Could benefit from more modularization (e.g., separating data, model, and utility modules).
-
GUI/Interactive Tools
- No GUI or dashboard for model interaction or result visualization.
Role Suitability¶
Best Fit Roles¶
-
Machine Learning Engineer / Data Scientist
- Strong evidence of end-to-end ML workflow, advanced modeling, and evaluation on real-world, imbalanced data.
- Experience with model explainability, compliance, and reproducibility.
-
ML Research/Prototyping
- Demonstrated ability to experiment with multiple models, hyperparameter tuning, and reporting.
-
Technical Documentation Specialist
- High-quality, clear, and comprehensive documentation and presentation materials.
Well-Suited For¶
-
ML/AI Competition Participant
- Familiarity with competition constraints, anonymization, and reproducibility.
-
Data Analyst (Advanced)
- Strong EDA, feature engineering, and reporting skills.
Less Suited For¶
- DevOps Engineer / MLOps
- No evidence of CI/CD, containerization, or production deployment.
- Backend/API Developer
- No API or backend service implementation.
- Frontend/GUI Developer
- No GUI or dashboard development.
Summary:
The developer demonstrates strong skills in machine learning engineering, with a focus on robust, reproducible pipelines for imbalanced binary classification. Strengths include advanced modeling, compliance, documentation, and explainability. The codebase is best suited for ML engineering, data science, and technical documentation roles. Areas for growth include automated testing, CI/CD, deployment, and software engineering best practices. The developer is less suited for DevOps, backend, or frontend roles based on the current evidence.
-
This AI skill assessment was generated based on the skill-assessment-prompt.md and the provided project documentation. It is intended as an illustrative summary and should be interpreted in the context of the available code and documentation in codebase. ↩